
Bcl-2
sequences
Sequences in FASTA Format
FASTA is a protein and DNA sequence alignment software package. Given a nucleotide or amino acid sequence, FASTA can search through a database to find matches of similar sequences. The results of this search are given in FASTA format, which is a text-based format for representing the nucleotide or peptide sequences by representing the base pairs or amino acids using their corresponding single-letter codes.
Representative Proteins
Bcl-2 Alpha
For further information about Bcl-2, see the page on its biological role.
MAHAGRTGYDNREIVMKYIHYKLSQRGYEWDAGDVGAAPPGAAPAPGIFSSQPGHTPHPAASRDPVARTSPLQTPAAPGAAAGPALSPVPPVVHLTLRQAGDDFSRRYRRDFAEMSSQLHLTPFTARGRFATVVEELFRDGVNWGRIVAFFEFGGVMCVESVNREMSPLVDNIALWMTEYLNRHLHTWIQDNGGWDAFVELYGPSMRPLFDFSWLSLKTLLSLALVGACITLGAYLGHK
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_000624.2
Bcl-2 Beta
For further information about Bcl-2, see the page on its biological role.
MAHAGRTGYDNREIVMKYIHYKLSQRGYEWDAGDVGAAPPGAAPAPGIFSSQPGHTPHPAASRDPVARTSPLQTPAAPGAAAGPALSPVPPVVHLTLRQAGDDFSRRYRRDFAEMSSQLHLTPFTARGRFATVVEELFRDGVNWGRIVAFFEFGGVMCVESVNREMSPLVDNIALWMTEYLNRHLHTWIQDNGGWVGALGDVSLG
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_000648.2
BAK
Bak is a multi BH domain pro-apoptotic protein. It is able to translocate to the outer mitochondrial membrane and become activated to form homodimers and subsequently oligomers that constitute towards the permeability transition pore.
MASGQGPGPPRQECGEPALPSASEEQVAQDTEEVFRSYVFYRHQQEQEAEGVAAPADPEMVTLPLQPSSTMGQVGRQLAIIGDDINRRYDSEFQTMLQHLQPTAENAYEYFTKIATSLFESGINWGRVVALLGFGYRLALHVYQHGLTGFLGQVTRFVVDFMLHHCIARWIAQRGGWVAALNLGNGPILNVLVVLGVVLLGQFVVRRFFKS
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/AAA74466.1
BAX
Bax is similar in structure and function to Bak. It is also a multi BH domain pro-apoptotic protein. It is able to translocate to the outer mitochondrial membrane and become activated to form homodimers and subsequently oligomers that constitute towards the permeability transition pore.
MDGSGEQPRGGGPTSSEQIMKTGALLLQGFIQDRAGRMGGEAPELALDPVPQDASTKKLSECLKRIGDELDSNMELQRMIAAVDTDSPREVFFRVAADMFSDGNFNWGRVVALFYFASKLVLKALCTKVPELIRTIMGWTLDFLRERLLGWIQDQGGWGLPLAESLKRLMSLSPGRPPLLLWDAHVADRDHLCGGSAHRLTHHLEEDGLRPPAALDCVFPP
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_001278357.1
PUMA
Puma is a BH3-only protein which acts to activate apoptosis by neutralising Bcl-2. It is upregulated by p53 in response to DNA damage. This abrogates the inhibitory functions of Bcl-2 over Bak and Bax in the formation of the apoptosis associated permeability transition pore.
MARARQEGSSPEPVEGLARDGPRPFPLGRLVPSAVSCGLCEPGLAAAPAAPTLLPAAYLCAPTAPPAVTAALGGSRWPGGPRSRPRGPRPDGPQPSLSLAEQHLESPVPSAPGALAGGPTQAAPGVRGEEEQWAREIGAQLRRMADDLNAQYERRRQEEQQRHRPSPWRVLYNLIMGLLPLPRGHRAPMEPN
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_055232.1
NOXA
Noxa is a small BH3-only protein which is pro-apoptotic in function. It is upregulated via the actions of p53 in response to DNA damage. Noxa can bind and neutralise Bcl-2 which leads to Bak and Bax activation and formation of the permeability transition pore.
MPGKKARKNAQPSPARAPAELEVECATQLRRFGDKLNFRQKLLNLISKLFCSGT
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_066950.1
BIM
Bim is a pro-apoptotic BH3 only protein. It negates the cell from undergoing apoptosis when the cell is subject to survival factor withdrawal. It neutralises Bcl-2 through its BH3 domain.
MAKQPSDVSSECDREGRQLQPAERPPQLRPGAPTSLQTEPQGNPEGNHGGEGDSCPHGSPQGPLAPPASPGPFATRSPLFIFMRRSSLLSRSSSGYFSFDTDRSPAPMSCDKSTQTPSPPCQAFNHYLSAMASMRQAEPADMRPEIWIAQELRRIGDEFNAYYARRVFLNNYQAAEDHPRMVILRLLRYIVRLVWRMH
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/O43521.1
HRK
HRK is a small BH3-only protein and its expressed is induced by JNK as a result of survival factor withdrawal. It is able to translocate to the outer mitochondrial membrane to neutralise Bcl-2 within the indirect model of activation of apoptosis, allowing the permeability transition pore formation.
MCPCPLHRGRGPPAVCACSAGRLGLRSSAAQLTAARLKALGDELHQRTMWRRRARSRRAPAPGALPTYWPWLCAAAQVAALAAWLLGRRNL
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_003797.1
Bcl-xL
Bcl-xL is an antiapoptotic multi-BH domain protein. Bcl-xL prevents Bak and Bax to form oligomers within the permeability transition pore that mediates the release of cytochrome C that leads to apoptosis initiation.
MSQSNRELVVDFLSYKLSQKGYSWSQFSDVEENRTEAPEGTESEMETPSAINGNPSWHLADSPAVNGATAHSSSLDAREVIPMAAVKQALREAGDEFELRYRRAFSDLTSQLHITPGTAYQSFEQVVNELFRDGVNWGRIVAFFSFGGALCVESVDKEMQVLVSRIAAWMATYLNDHLEPWIQENGGWDTFVELYGNNAAAESRKGQERFNRWFLTGMTVAGVVLLGSLFSRK
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/O43521.1
Mcl-1
Mcl-1 is an antiapoptotic multi-BH domain protein. Mcl-1 prevents Bak and Bax to form oligomers within the permeability transition pore that mediates the release of cytochrome C that leads to apoptosis initiation.
MFGLKRNAVIGLNLYCGGAGLGAGSGGATRPGGRLLATEKEASARREIGGGEAGAVIGGSAGASPPSTLTPDSRRVARPPPIGAEVPDVTATPARLLFFAPTRRAAPLEEMEAPAADAIMSPEEELDGYEPEPLGKRPAVLPLLELVGESGNNTSTDGSLPSTPPPAEEEEDELYRQSLEIISRYLREQATGAKDTKPMGRSGATSRKALETLRRVGDGVQRNHETAFQGMLRKLDIKNEDDVKSLSRVMIHVFSDGVTNWGRIVTLISFGAFVAKHLKTINQESCIEPLAESITDVLVRTKRDWLVKQRGWDGFVEFFHVEDLEGGIRNVLLAFAGVAGVGAGLAYLIR
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_068779.1
D. melanogaster Bcl-2 death executioner: The fruit fly Bcl-2 protein homologue
>NP_788278.1 death executioner Bcl-2 [Drosophila melanogaster]
MAPTTSPPPKLAKFKSSSLDHEIYTANRRGTIATASSDWKALRGGVGGGAGGPGSVPNPSNGRSLHAGGPMTRAASTSSLASSTRTMTNYQEYKMDIINQGKCLCGQYIRARLRRAGVLNRKVTQRLRNILDPGSSHVVYEVFPALNSMGEELERMHPRVYTNISRQLSRAPFGELEDSDMAPMLLNLVAKDLFRSSITWGKIISIFAVCGGFAIDCVRQGHFDYLQCLIDGLAEIIEDDLVYWLIDNGGWLGLSRHIRPRVGEFTFLGWLTLFVTISAGAYMVSNVCRRIGGQLYSLLF
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_788278.1
C. elegans CED-9: The nematode Bcl-2 protein homologue
>sp|P41958|CED9_CAEEL Apoptosis regulator ced-9 OS=Caenorhabditis elegans GN=ced-9 PE=1 SV=1
MTRCTADNSLTNPAYRRRTMATGEMKEFLGIKGTEPTDFGINSDAQDLPSPSRQASTRRMSIGESIDGKINDWEEPRLDIEGFVVDYFTHRIRQNGMEWFGAPGLPCGVQPEHEMMRVMGTIFEKKHAENFETFCEQLLAVPRISFSLYQDVVRTVGNAQTDQCPMSYGRLIGLISFGGFVAAKMMESVELQGQVRNLFVYTSLFIKTRIRNNWKEHNRSWDDFMTLGKQMKEDYERAEAEKVGRRKQNRRWSMIGAGVTAGAIGIVGVVVCGRMMFSLK
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/AAA20080.1
Model Organisms
H. sapiens Bcl-2 ALPHA isoform: The human Bcl-2 protein
>NP_000624.2 apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 alpha isoform [Homo sapiens]
MAHAGRTGYDNREIVMKYIHYKLSQRGYEWDAGDVGAAPPGAAPAPGIFSSQPGHTPHPAASRDPVARTSPLQTPAAPGAAAGPALSPVPPVVHLTLRQAGDDFSRRYRRDFAEMSSQLHLTPFTARGRFATVVEELFRDGVNWGRIVAFFEFGGVMCVESVNREMPLVDNIALWMTEYLNRHLHTWIQDNGGWDAFVELYGPSMRPLFDFSWLSLKTLLSLALVGACITLGAYLGHK
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_000624.2
M. musculus Bcl-2 Isoform 1: The house mouse Bcl-2 protein homologue
>NP_033871.2 apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 isoform 1 [Mus musculus]
MAQAGRTGYDNREIVMKYIHYKLSQRGYEWDAGDADAAPLGAAPTPGIFSFQPESNPMPAVHRDMAARTSPLRPLVATAGPALSPVPPVVHLTLRRAGDDFSRRYRRDFAEMSSQLHLTPFTARGRFATVVEELFRDGVNWGRIVAFFEFGGVMCVESVNREMSPLVDNIALWMTEYLNRHLHTWIQDNGGWDAFVELYGPSMRPLFDFSWLSLKTLLSLALVGACITLGAYLGHK
Link To Flat File: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_033871.2
BLAST stands for ‘Basic Local Alignment Search Tool’, and it is an algorithm for comparing primary biological sequence information, such as protein amino acid sequences or DNA nucleotide sequences. BLAST searches allow for comparison of a sequence with a database of other sequences, and it can identify statistically significant sequence matches.
BLAST Searches and Analysis
H. sapiens Bcl-2 ALPHA Isoform
Conserved Domains
Distribution of the Top 100 Blast Hits on 100 Subject Sequences

Sequences Producing Significant Alignments

The E value describes the number of hits one can expect to see randomly or by chance. As the score of the match increases, the E value will decrease. For the alpha isoform in H. sapiens, we have no E values of zero, but other forms of the protein, including those found in other species are shown to have very low E values and thus a high match score.
H. sapiens Bcl-2 BETA Isoform
Conserved Domains

Distribution of the Top 100 Blast Hits on 100 Subject Sequences

Sequences Producing Significant Alignments

The E value describes the number of hits one can expect to see randomly or by chance. As the score of the match increases, the E value will decrease. For the beta isoform in H. sapiens, we have no E values of zero, but other forms of the protein found in H. sapiens are shown to have very low E values and thus a high match score.
Representative Proteins
Bcl-xL

Mcl-1
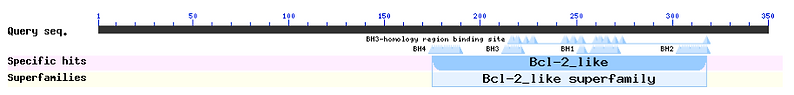
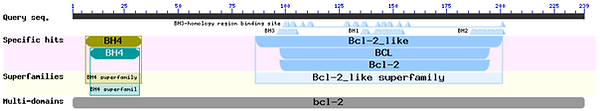
From BLAST searches of Bcl-xL and Mcl-1, we can see that both proteins contain all four BH domains (BH1-4) and can therefore be considered as members of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family.
Interestingly, both proteins have the BH domains in the same order, with BH4 first, then BH3, then BH1 and finally BH2. However, Bcl-xL has the BH4 domain at the N terminus, and it belongs to the BH4 superfamily. Although Mcl-1 has a BH4 domain, it is closer to the middle of the protein and it is not shown to have the sequence overlap necessary to belong to the superfamily. Additionally, Bcl-xL is shown to be likely to contain multiple single Bcl-2 domains, while Mcl-1 is not shown to have any multi-domains.
Multiple Sequence Alignments and Analysis
A Multiple Sequence Alignment is a comparison of several DNA or amino acid sequences. It can be used to suggest and identify the presence of evolutionary relationships between the sequences, such as that from a shared lineage or common ancestor. The results can also suggest sequence homology, or a region that has been conserved among multiple sequences, which may indicate a particular importance or function for that domain.
It is possible to use comparative multiple sequence alignments for Bcl-2 with initially pro-apoptotic BH3 only proteins and secondly Bcl-2 with multiple domain pro-apoptotic proteins and anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bak, Bax, Mcl-1 and Bcl-xl all of homo sapiens. In doing so, this may it possible to highlight a plausible BH3 domain location for the Bcl-2 protein. It appears the BH3 domain for Bcl-2 is between amino acid residues 86 (leucine) to 108 (tyrosine). In view of the multiple sequence alignment of Bcl-2 with Bak, Bax, Mcl-1 and Bcl-xl. There are multiple regions of high homology which would likely account for the array of Bcl-2 homology domains (BH domains) as well as a C-terminal transmembrane domain. There is a proximal N-terminal region of homology for Bcl-2, Bcl-xl and Mcl-1 proteins suggesting BH domain lacked by Bak and Bax pro-apoptotic proteins. This proves to be the BH4 domain. This can be further compounded by blast search analysis.
Within proteins of the Bcl-2 family there are regions of homology represented as Bcl-2 homology domain (BH domains), these range from BH1-4. BH3 only possession is a marked property of neutralising pro-apoptotic proteins such as Puma, Bim and Noxa. Proteins that confer BH1-3 domains include Bax and Bak of whom are also pro-apoptotic in nature. A subset of proteins of the Bcl-2 family include an additional BH4 domain and these are described as anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2, Mcl-2 and Bcl-xl. All Bcl-2 family proteins contain a C-terminus transmembrane domain consisting of a series of hydrophobic residues that permits localisation to the outer mitochondrial membrane. The hydrophobic grove is contributed towards BH1, BH2 and BH3 domains. In terms of function a high degree of homology here closely represents the functions of multiple Bcl-2 family proteins, in particular Bcl-2 itself, as this groove is used as the mediator of interactions of other proteins such as Bcl-2 with Bak/Bax or Bax and Bak themselves to form homodimers. The BH3 domain also is highly conserved, also not surprising given that it inserts into this hydrophobic groove multiple making hydrophobic contacts and hydrogen bonds as an amphipathic alpha-helix. The BH4 domain is a lot less common, and until recently its functionality behind its conservation appeared elusive. It is now believed to facilitate autophagosome formation.
References:
[1] Kvansakul, M. & Hinds, M.G. Apoptosis (2015) 20: 136. doi:10.1007/s10495-014-1051-7 [Pubmed]
[2] Jiang T, Liu M, Wu J, Shi Y. Structural and biochemical analysis of Bcl-2 interaction with the hepatitis B virus protein HBx. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2016;113(8):2074-2079. doi:10.1073/pnas.1525616113. [Pubmed]
[3] Trisciuoglio D, De Luca T, Desideri M, et al. Removal of the BH4 Domain from Bcl-2 Protein Triggers an Autophagic Process that Impairs Tumor Growth. Neoplasia (New York, NY). 2013;15(3):315-327. [Pubmed]
Further Domain Information

