
Bcl-2
Structure
Animation of Structure and Active Site of Bcl-2
Structure of the Bcl-2 Active Site
Bcl-2 contains 5 conserved domains that can be found in all members of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family: Bcl-2 Homology (BH) domains 1-4 and a transmembrane domain located at the C-terminus. In addition to the conserved domains, the protein consists of 7 alpha helices, where the two central predominantly hydrophobic helices (helix 5 and 6) are wrapped around 4 amphipathic helices (see animation above). The active side of Bcl-2 is formed by alpha helices 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7. It is a hydrophobic groove on the surface called BH3-binding groove (also called the hydrophobic groove).
For further information about the Bcl-2 domains, click here.
Structure Modelling and Analysis
For the analysis of the structure of Bcl-2, the isoform “Bcl-2 Alpha Isoform [Homo sapiens]” would have been the most representative protein to be used. However, since the sequence in its current form has only been established in 2016 no crystallography-determined PDB file has been created.
Group 7 tried to circumvent this problem by using the structure prediction software Swissmodel. Using the FASTA sequence of “Bcl-2 Alpha Isoform [Homo sapiens]” we created the Protein structure seen in Figure 1 and Figure 2.

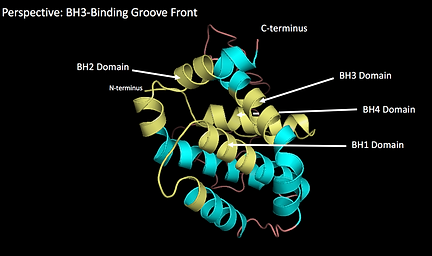
Figure 1
Figure 2
This structure, however, does not show the transmembrane region of the protein because the software automatically finds the closest matching already existing PDB file and predicts the new sequence based on this file with a standard algorithm.
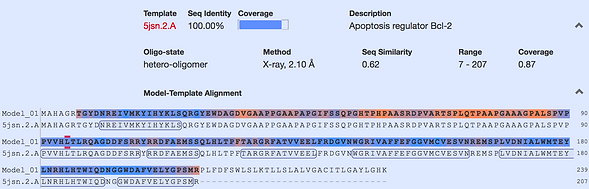
Figure 3 shows the result of this process. The sequence of “Bcl-2 Alpha Isoform [Homo sapiens]” (marked as Model_01) matched with the already existing protein PDB file “Chain A, Human Bcl-2, Isoform 1” (marked as 5jsn.2.A) shows that the latter has a 100% identical sequence with the former. “Bcl-2 Alpha Isoform [Homo sapiens]”, however has additional regions not seen in the
Figure 3
empirically determined “Chain A, Human Bcl-2, Isoform 1”. Since the structure (Fig. 1,2) is computer generated we cannot guarantee that the real protein looks like this.
We, therefore, used the structure of “Chain A, Human Bcl-2, Isoform 1” as established by Petros et al (2001). It has to be said that Petros et al. used a Bcl-2/Bcl-xL chimera protein that differs in two ways from the recently sequenced “Bcl-2 Alpha Isoform [Homo sapiens]”: Firstly, for determining the structure of the chimera, the putative unstructured loop of Bcl-2 was replaced with a shortened loop from Bcl-xL as can be seen in Figure 4 and Figure 5. Secondly, the transmembrane domain has been neglected in this model.

Figure 4 - RCSB PDB

Figure 5 - RCSB PDB
This leads to the structure of “Chain A, Human Bcl-2, Isoform 1” being merely 166 aa long, in comparison to the 239 aa long “Bcl-2 Alpha Isoform [Homo sapiens]”. Nevertheless, by looking at the relevant BLASTs, we can see that “Chain A, Human Bcl-2, Isoform 1” still exhibits all 4 BH-domains and still forms a functional BH3-binding groove.
Hence, even though this isolated form could not by itself function in vivo because no localisation of the protein to the outer mitochondrial membrane would be observed since the transmembrane domain is missing, we can still use the structure to gain vital insights into the function of Bcl-2.
BLAST of Bcl-2 Alpha Isoform [Homo sapiens]

BLAST of Chain A, Human Bcl-2, Isoform 1

The original PDB file used to create the structure models was 1G5M and can be downloaded directly from the RCSB site [RCSB PDB]. Additionally, we extracted the structure coordinate values using Matlab and saved the data onto a word document, which can be downloaded here.
Visual Representation of BH Domains
The animation above was created to show the BH domains on the 3D structure of the protein.
References:
[1] Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 alpha isoform [Homo sapiens] [FLAT]
[2] Chain A, Human Bcl-2, Isoform 1 [FLAT] [RCSB PDB]
[3] Petros AM, Medek A, Nettesheim DG, et al. Solution structure of the antiapoptotic protein bcl-2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001;98(6):3012-3017. doi:10.1073/pnas.041619798. [PubMed]
This model has been created by a Swissmodel predicted version of BAX isoform 1 and PDB 1G5M.
The hydrophobic BH3-binding groove of Bcl-2 has been labelled yellow. Bax’s BH3-domain is marked in brown. Bcl-2’s BH3-binding groove binds Bax’s BH3-domain via van der Waals interactions and can establish relatively strong binding with a Kd of 15.1 nM. This ensures that the pro-apoptotic protein Bax is not easily released and mitochondrial permeability stays low.
References:
[1] Apoptosis regulator BAX isoform 1 [Homo sapiens] [FLAT]
[2] Ku B, Liang C, Jung JU, Oh B-H. Evidence that inhibition of BAX activation by BCL-2 involves its tight and preferential interaction with the BH3 domain of BAX. Cell Research. 2011;21(4):627-641. doi:10.1038/cr.2010.149. [PubMed]
Example Interaction: Model of Bax Bound to Bcl-2
